Joining a Windows Client or Server to a Domain
Introduction
After setting up a Samba Active Directory (AD) or an Samba NT4 domain, you have to join machines to the domain. Only machines joined to the domain are enabled to use domain resources. During the join, a machine account is created in the domain to authenticate the computer as a member.
In case, you are joining a Windows Server as a domain controller (DC) to an AD, see:
- Joining a Windows Server 2008 / 2008 R2 DC to a Samba AD
- Joining a Windows Server 2012 / 2012 R2 DC to a Samba AD
Use this documentation for joining a Windows client or server operating system to a Samba AD or Samba NT4 domain as a domain member.
System Requirements
Supported Windows Versions
To join a domain, the Windows edition requires the corresponding capabilities. You can join the following Windows operating systems as a domain member:
Workstation editions:
- Windows 10: Pro, Enterprise, and Education
- Windows 8 and 8.1: Pro and Enterprise
- Windows 7: Professional, Ultimate, and Enterprise
- Windows Vista: Business, Ultimate, and Enterprise
- Windows XP: Professional
- Windows 2000: Professional
- Windows NT4 (only NT4 domain support)
Server (all editions):
- Windows Server 2019
- Windows Server 2016
- Windows Server 2012 and 2012R2
- Windows Server 2008 and 2008R2
- Windows Server 2003 and 2003R2
- Windows Server 2000
Permissions
To join a machine to a domain you require:
- local administrator permissions on the computer you want to join
- credentials of a domain account that is enabled to join machines to the domain. For example:
- the domain administrator account
- an account with delegated permissions (AD only)
- Note, that in an AD authenticated user accounts are enabled to join up to 10 machines to the domain, if the administrator has not disabled the feature. See https://support.microsoft.com/kb/243327/en
Required Settings for NT4 Domains
If you are joining the host to a Samba NT4 domain, some Windows operating systems require modifications. See Required Settings for Samba NT4 domain.
DNS Settings (AD only)
In an Active Directory (AD), a working DNS configuration is indispensable. AD uses DNS to locate domain controllers (DC), resolve host names, and for many other tasks. Ensure that the client has at least one DNS server configured, that is able to resolve the AD DNS zone. For further information, see DNS Configuration on Windows Hosts.
Date and Time Settings (AD only)
Active Directory uses Kerberos for authentication. Kerberos requires that the domain member and the domain controllers (DC) are having a synchronous time. If the difference exceeds 5 minutes (default), the client is not able to access domain resources for security reasons.
Before you join the domain, check the time configuration:
- Open the
Control Panel.
- Navigate to
Clock, Language and Region.
- Click
Date and Time.
- Verify the date, time, and time zone settings. Adjust the settings, if necessary.
- Click
OKto save the changes.
Joining a Windows Client or Server to a Domain
- Open the
Control Panel.
- Navigate to
System and Security/ System.
- Click
Change settings, next to the computer name.
- On the
Computer Nametab, click theChangebutton.
- Verify the computer name. If you rename the computer, reboot before joining the domain.
- Select
Domain, enter the name of your domain, and clickOK.
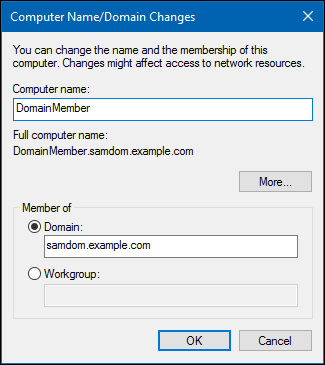
- Active Directory (AD) only: You can enter the NetBIOS name of the domain, if your client is able to resolve it. For example:
samdominstead ofsamdom.example.com.
- Enter the credentials of an account that is able to join a computer to the domain. For example, the domain administrator account. Click
OKto continue.
- Reboot the computer after the computer successfully joined the domain.