Wireshark Decryption
Using the session key (SMB3+)
Starting from Wireshark 2.5.0 (released Feb 2018) you can pass a list of SessionId -> SessionKey mappings via a table in the SMB2 preferences or command-line.
The session key in this context refers to the cryptographic session keys used in authentication and message signing. It is not the same as the CIFS SessionKey.
From MS-SMB2:
Session.SessionKey: The first 16 bytes of the cryptographic key for this authenticated context. If the cryptographic key is less than 16 bytes, it is right-padded with zero bytes.
Known limitations
- SMB3.0 AES-128 CCM decryption added in Wireshark 2.6.5 (December 2018)
- SMB3.1.1 AES-128 CCM decryption added in Wireshark 3.0.0 (February 2019)
- AES-128 GCM for SMB3.1.1 added in Wireshark 3.1.0 (July 2019)
- Before Wireshark 3.3.0 (September 2020): Due to how key generation works, the trace needs to have the initial connection packets (NegProt and SessSetup) present in the trace being decrypted (done using the right session id).
- Starting from 3.3.0, you can directly provide the decryptions keys, NegProt and SessSetup don't have to be in the trace.
- Wireshark needs to be built with libgcrypt >= 1.6.0. (you can check in
wireshark -voutput) - Support for multichannel decryption added in Wireshark 3.3.0 (September 2020).
- No AES-256 support yet.
You can test with the sample traces on the Wireshark wiki. If decryption doesn't work on those some of the requirement mentioned above are not met.
Using the server and client decryption keys (SMB3+)
Starting from Wireshark 3.3.0 (released Sept 2020) you can pass a list of SessionId => ServerKey,ClientKey via the table in the SMB2 preferences or command-line. As a result the syntax to provide them changed.
If you are unsure of which key is the server and which key is the client it doesn't matter Wireshark will try both.
By passing directly the decryption keys instead of the session key wireshark doesn't require the session establishment packets (NegProt & Session Setup) to be in the capture.
The CLI syntax to provide keys has changed to allow providing any combinations of SessionKey, ServerToClientKey, ClientToServerKey:
tshark -Y smb2 '-ouat:smb2_seskey_list:<sessionid>,<session key>,<server to client key>,<client to server key>' -r trace.pcap
If you are missing one you can skip it by using the empty string "". For example:
tshark -Y smb2 '-ouat:smb2_seskey_list:0502004c955a1080,a3c0338caf84f4a254445a9724f1c462,"",""' -r trace.pcap
Obtaining the keys
Linux kernel client
For more recent Linux kernels (feature was added in September 2019, Linux kernel version 5.4) SMB3 cryptographic keys can be dumped by using the utility smbinfo (must be run as root or CAP_SYS_ADMIN, cifs-utils version 6.10):
smbinfo keys <path-to-a-file-on-an-smb3-mount>
For older kernels the linux client (cifs.ko) can be configured to dump the cryptographic keys it generates (visible in dmesg output) via the build time option CONFIG_CIFS_DEBUG_DUMP_KEYS. Keep in mind this is a debugging option and it should not be set on a production system.
You can set this option in your .config file or find it in make menuconfig by going in:
- File systems
- Network File Systems
- SMB3 and CIFS support (advanced network filesystem)
- Enable CIFS debugging routines > Dump encryption keys for offline decryption (Unsafe).
- SMB3 and CIFS support (advanced network filesystem)
- Network File Systems
Once enabled, you can mount a share and pass the mount options vers=3 or vers=3.11 to make sure the connection uses SMB3 and seal to require encryption.
If the connection reaches the Tree Connect stage you should be able to see this in the kernel console (via dmesg) for each session established:
CIFS VFS: generate_smb3signingkey: dumping generated AES session keys CIFS VFS: Session Id bc 1a fc 0d 00 00 00 00 CIFS VFS: Session Key 34 57 e1 90 4b 94 3a 0d 09 be 22 b9 b9 cf c7 4c CIFS VFS: Signing Key 28 bf a3 71 39 e5 05 71 c6 15 58 f3 cf 42 3f 0e CIFS VFS: ServerIn Key 79 2a 9a 40 1e cf 16 52 41 a5 ec bd 1c e5 84 17 CIFS VFS: ServerOut Key c0 73 c8 1d 36 f5 74 3e ef 6e c1 9d 5c e5 cb 71
Samba client and server
Starting from Samba 4.11, both client and server code can dump the generated keys in the log file using "debug encryption = yes" in smb.conf or via the command line. Note that when given via smb.conf, the option controls both server and client code.
Example:
$ smbclient //localhost/scratch --option='debugencryption=yes' -e -mSMB3 -U aaptel%aaptel
debug encryption: dumping generated session keys
Session Id [0000] F0 38 C7 30 00 00 00 00 .8.0....
Session Key [0000] CB 18 C5 26 18 CA 9F 59 44 0A 62 44 63 90 2B BA ...&...Y D.bDc.+.
Signing Key [0000] A6 0B B1 50 1B FD 51 1F 8A 06 00 8C 13 7E 7C 4F ...P..Q. .....~|O
ServerIn Key [0000] 7D 93 ED 2D E6 54 0C 86 8F 3F B5 AE 63 1D BD E7 }..-.T.. .?..c...
ServerOut Key [0000] 7A D0 18 61 7B E3 E5 2A 33 5E 27 66 D1 6B F9 0E z..a{..* 3^'f.k..
Setting the key
Note: The kernel prints the Session Id as it is on the wire (little endian). Wireshark decryption expects the Session Id as it is on the wire as well, so you should be able to copy/paste from one to the other (despite showing the Session ID field decoded when dumping packets).
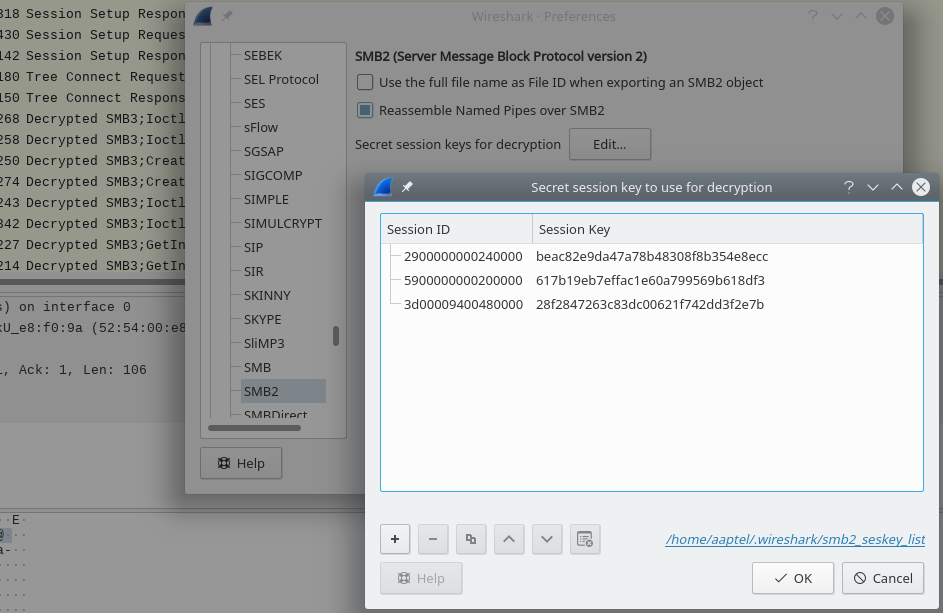
- Just copy the Session Id and Session Key into wireshark (see screenshot).
- Alternatively you can pass them via the command line (works with wireshark and tshark):
# Wireshark version pre-3.3.0 tshark -ouat:smb2_seskey_list:3d00009400480000,28f2847263c83dc00621f742dd3f2e7b -r smb3-aes-128-ccm.pcap # Wireshark version 3.3.0 and above tshark '-ouat:smb2_seskey_list:3d00009400480000,28f2847263c83dc00621f742dd3f2e7b,"",""' -r smb3-aes-128-ccm.pcap
Using a keytab
Prerequisite
You only need to do that once:
- Open Wireshark
- Goto: Preferences -> Protocols -> KRB5
- Select: Try to decrypt encrypted Kerberos blobs
Basic decryption
The easiest way, on a unix-like system is to run
wireshark -K <PATH TO KEYTAB> <PCAP FILE>
Note: Wireshark for 64-bit Windows (GUI or command-line) doesn't like the -K flag, run the 32-bit Windows version instead.
The other way, is to specify the keytab in Preferences -> Protocols -> KRB5 -> keytab path
How to extract the keytab?
See: How to extract a keytab from a windows domain with Samba
Decrypted AES DCE/RPC
To do this, you will need wireshark 3.3.0 or later. Build from source or git if you don't have this version or later.
Better (encrypted) DRSUAPI decode
The best way to read DRSUAPI in wireshark is to use the branch by metze. This is based on wireshark master and at the time of writing (using ws-metze/20221103) these commands were required to build it on Ubuntu 20.04:
CC="ccache gcc" cmake ../ -G Ninja -DUSE_qt6=OFF -Wno-error=dev -Wno-dev -DENABLE_WERROR=No ninja